Introduction
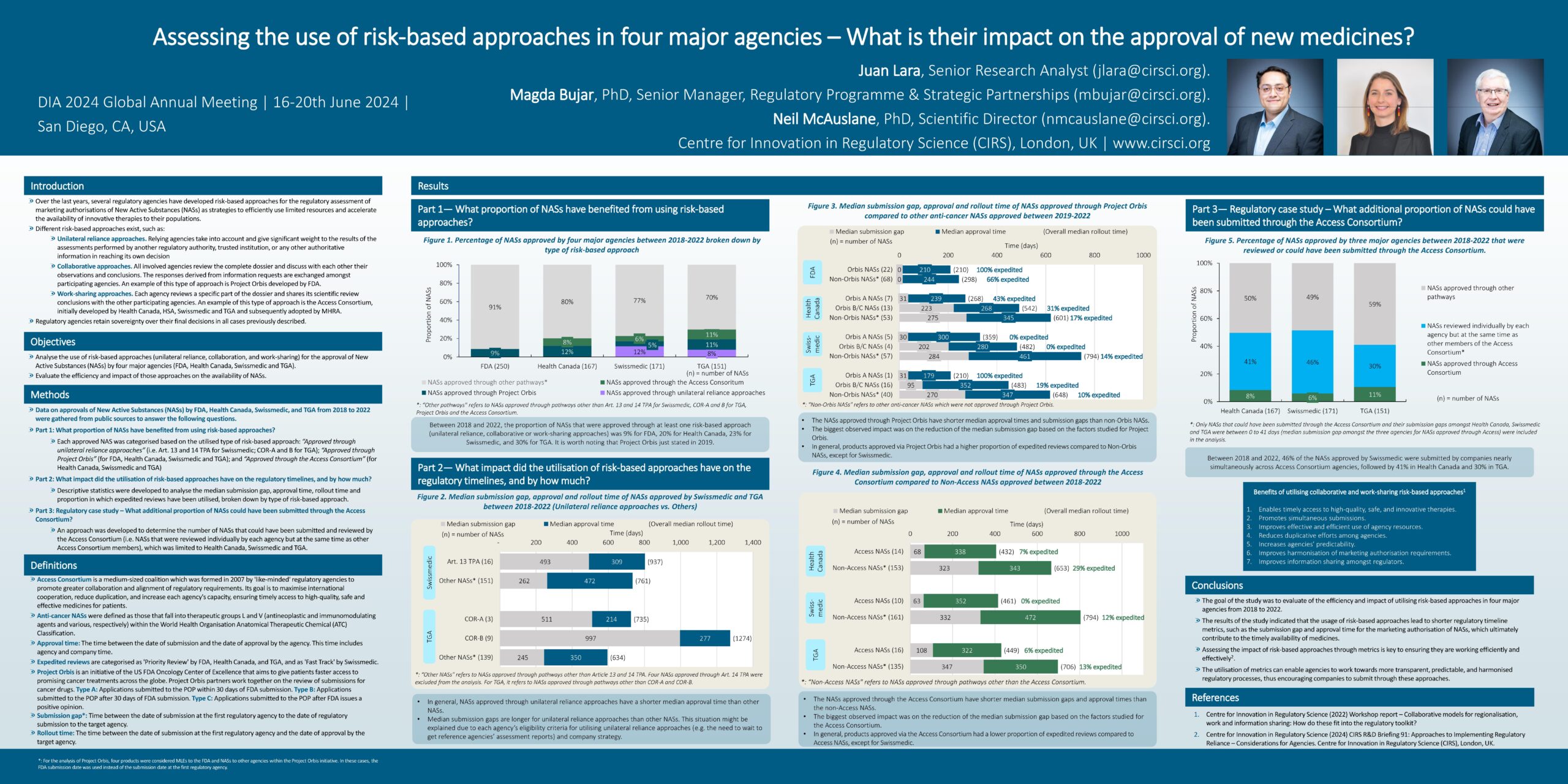
Over the last years, several regulatory agencies have developed risk-based approaches for the regulatory assessment of marketing authorisations of New Active Substances (NASs) as strategies to efficiently use limited resources and accelerate the availability of innovative therapies to their populations.
Different risk-based approaches exist, such as:
- Unilateral reliance approaches: Relying agencies take into account and give significant weight to the results of the assessments performed by another regulatory authority, trusted institution, or any other authoritative information in reaching its own decision
- Collaborative approaches: All involved agencies review the complete dossier and discuss with each other their observations and conclusions. The responses derived from information requests are exchanged amongst participating agencies. An example of this type of approach is Project Orbis developed by FDA.
- Work-sharing approaches: Each agency reviews a specific part of the dossier and shares its scientific review conclusions with the other participating agencies. An example of this type of approach is the Access Consortium, initially developed by Health Canada, HSA, Swissmedic and TGA and subsequently adopted by MHRA.
Regulatory agencies retain sovereignty over their final decisions in all three of these cases.
Study summary
- The goal of this CIRS study was to evaluate the efficiency and impact of utilising risk-based approaches in four major agencies from 2018 to 2022.
- The results of the study indicated that the usage of risk-based approaches lead to shorter regulatory timeline metrics, such as the submission gap and approval time for the marketing authorisation of NASs, which ultimately contribute to the timely availability of medicines.
- Assessing the impact of risk-based approaches through metrics is key to ensuring they are working efficiently and effectively.
- The utilisation of metrics can enable agencies to work towards more transparent, predictable, and harmonised regulatory processes, thus encouraging companies to submit through these approaches.
This poster was presented at the 2024 DIA Global Annual Meeting, 16-20th June 2024, San Diego, USA.