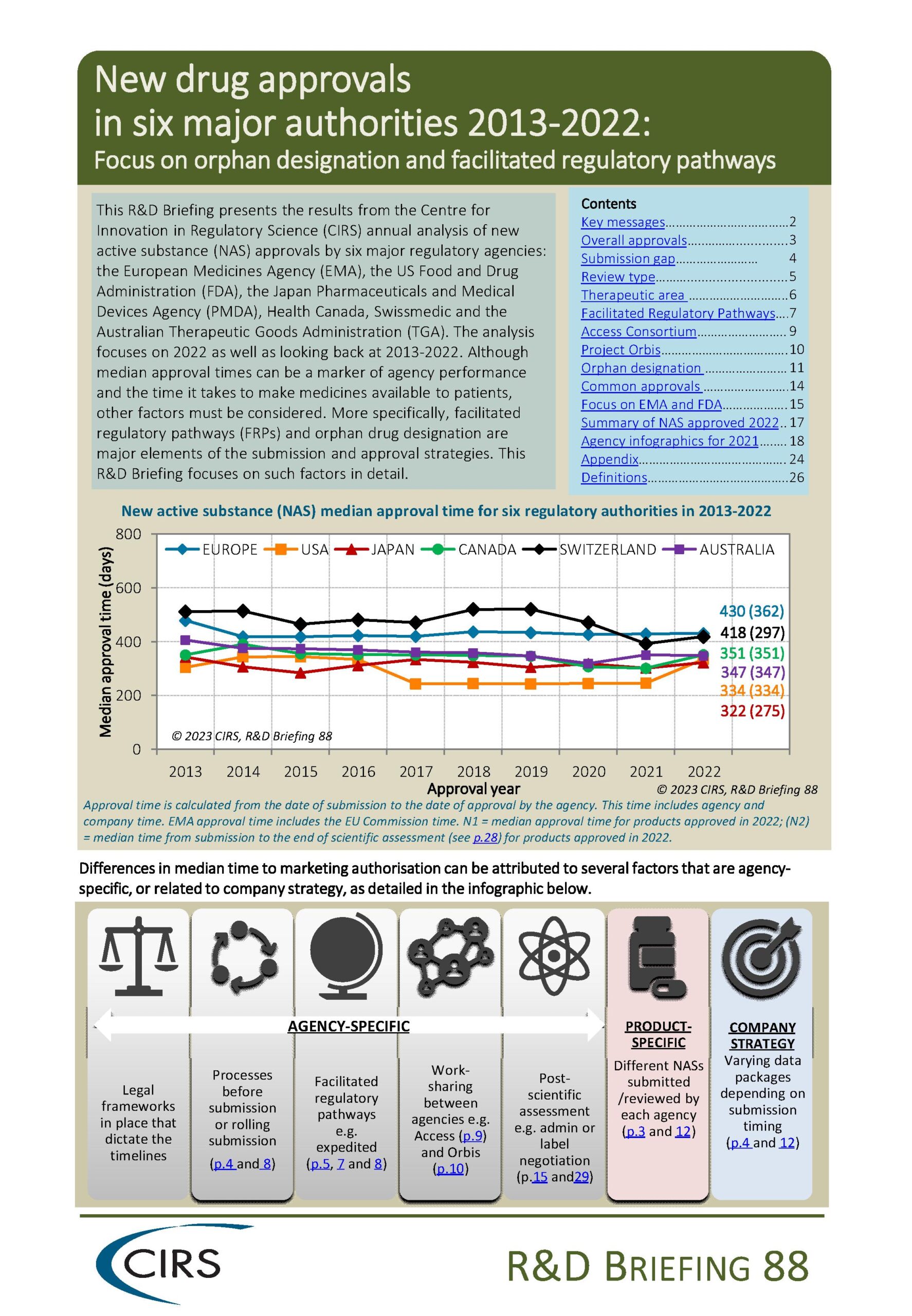
This R&D Briefing presents the results from the Centre for Innovation in Regulatory Science (CIRS) annual analysis of new active substance (NAS) approvals by six major regulatory agencies: the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Japan Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), Health Canada, Swissmedic and the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). The analysis focuses on 2022 as well as looking back at 2013-2022.
Although median approval times can be a marker of agency performance and the time it takes to make medicines available to patients, other factors must be considered. More specifically, facilitated regulatory pathways (FRPs) and orphan drug designation are major elements of the submission and approval strategies. This R&D Briefing focuses on such factors in detail.
The NAS list associated with this R&D Briefing is available to download here.
If you have any questions or comments on this R&D Briefing, please don’t hesitate to get in touch with Magda Bujar: mbujar@cirsci.org
Please cite this article as: Centre for Innovation in Regulatory Science (2023) R&D Briefing 88: New drug approvals in six major authorities 2013–2022: Focus on orphan designation and facilitated regulatory pathways. Centre for Innovation in Regulatory Science (CIRS), London, UK.