Publications
CIRS publishes insights from its research and meetings in several forms:
- R&D Briefings – research papers produced by the CIRS team e.g. annual regulatory and HTA benchmarking briefings
- Journal articles – peer reviewed academic research papers
- Reports – from CIRS workshops and externally commissioned research projects, as well as CIRS Annual Reports
- Books – research theses from CIRS-supported PhD students
- Posters – presented at external conferences
Keep up-to-date with CIRS publications and activities by signing up to our mailing list or following CIRS on LinkedIn.
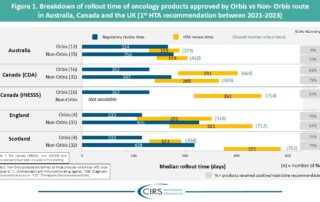
CIRS RD Briefing 96 – Review of HTA outcomes and timelines in Australia, Canada and the UK 2019-2023
This R&D Briefing presents data from HTADock, an ongoing metrics study that collects publicly available data on new active substances (NASs) appraised by key international HTA agencies. It focuses on …
Ngum 2024 – Evaluation of review models and timelines in the EAC-MRH
Introduction: Medicines regulatory harmonisation has been embraced by many national regulatory authorities (NRAs) to improve public health through faster availability of safe, high-quality, and effective medical products to patients and …
Ngum 2024 – Evaluation of good review practices in the EAC-MRH
Introduction: The East African Community Medicines Regulatory Harmonisation (EAC-MRH) programme was established to address challenges faced by national regulatory authorities (NRAs) of the region. Work sharing through joint assessments and …
Workshop Report – Vaccine regulatory and funding approaches
Over the last four years there has been much greater attention paid by industry, regulators, health technology assessment (HTA) bodies and the general public to vaccines for a range of …
Monitoring implementation and adherence to ICH guidelines
Background: This study was built on the previous 2019 and 2021 assessments where the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) selected CIRS to …
Workshop Report – Ensuring efficient and effective implementation of joint clinical assessment (JCA)
The Regulation (EU) 2021/2282 on health technology assessment (HTAR) reflects a significant step towards harmonising the clinical assessment in HTA decision making across EU Member States. It aims to improve …
2024 Workshop Synopsis – Evolving regulatory and funding approaches for vaccines
In this workshop, CIRS brought together senior representatives from the international pharmaceutical industry, regulatory agencies, National Immunisation Technical Advisory Groups (NITAGs), HTA agencies, payers and academia to identify challenges and …
Role of Regional Initiatives in the Operationalisation of the African Medicines Agency: Contribution of the EAC-MRH Initiative
“This book teaches us important lessons that we will need to consider in our collaboration work with the African Medicines Agency. I am confident that this research will be extremely …
2024 Workshop Synopsis – Ensuring efficient and effective implementation of joint clinical assessment (JCA)
In this workshop, CIRS brought together senior representatives from HTA agencies, pharmaceutical companies, payers and patient organisations to discuss their readiness for the EU HTA Regulation (HTAR) being applied from …
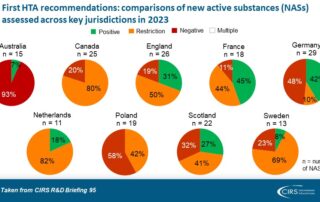
CIRS RD Briefing 95 – Review of HTA outcomes and timelines in Australia, Canada, Europe and the UK 2019-2023
This R&D Briefing presents data from HTADock, an ongoing metrics study that collects publicly available data on new active substances (NASs) appraised by key international HTA agencies, each with unique …
Rare Disease Product Approvals: The Changing Regulatory And HTA Landscape Between 2018-2022
Background Globally, 7,000 rare diseases affecting 300 million people pose development challenges with small patient populations. Developing medicines for rare diseases requires innovation. Despite regulatory incentives, challenges for HTA and …
2024 Workshop report – Reliance and regional review models
Faced with increasingly complex technologies and novel evidence generation techniques, regulatory agencies are being challenged to work in new ways. There is pressure on them to be agile and effective …